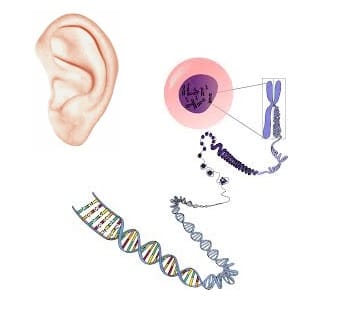
As much as 98% of the human genome does not code for protein. RNAs contained in this non-coding part act as regulatory molecules and have a substantial impact on gene expression. One type of these RNA molecules, called long non-coding RNAs, has been linked to a wide range of diseases and inheritable conditions such as cancer and celiac disease. Recently, a new Tel Aviv University study published in the esteemed scientific journal Nature shed light on critical piece of the puzzle of human deafness.
The study, published online in August 2017 identified the first group of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in the auditory and vestibular system.
Understanding Gene Expression and the Auditory System
As first reported in the December 17 issue of Bioscholar, Professor Karen Avraham of Tel Aviv University and a co-author of the paper said, “The research on long non-coding RNAs is crucial to understanding how gene expression and regulatory elements influence the auditory system. How do changes in these inheritable parts of the genome contribute to deafness? There is a need for new approaches and entry points to gene therapy. Knowing more about how genes are controlled may help devise strategies. Ours is the first report describing lncRNAs on a comprehensive level in a model of human deafness. This work provides a resource to look further into some of the lncRNAs and study their exact function in the inner ear — a key first step towards a potential cure,” Prof. Avraham says.
The researchers performed state-of-the-art next-generation sequencing (NGS) on a model of human deafness to identify the critical lncRNAs.
“We generated a whole-genome lncRNA profile to recognize differentially expressed lncRNAs in developing inner ear organ systems. The resulting catalog, which contains over 3,000 lncRNAs, summarizes for the first time their expression patterns across the auditory and vestibular systems. We focused our attention on three genes out of these lncRNAs. They were selected because of their proximity to genes related to hearing and deafness.” –Professor Karen Avraham, Tel Aviv University
According to the study, identifying the lncRNAs that play an unknown role in regulating genes involved in deafness will have an impact. “Recessive mutations causing disease — and deafness — continue to prevail, especially in the parts of the world where marriages take place between relatives, such as in the Middle East; this is known as ‘consanguinity,’” Prof. Avraham says. “LncRNAs are situated beside deafness genes, suggesting they direct and regulate these genes. By further examining these lncRNAs down the line, we may be able to help the hard of hearing, young and old alike.”
Inherited Deafness: Still Much Left to Study
“There are still a considerable number of unsolved inherited deafness cases, despite the use of NGS,” Prof. Avraham concludes. “This was what first led us to start an effort to identify novel genomic regulatory elements to explore the noncoding portion of the genome. Identifying such players can eventually assist in isolating pathogenic variants or regulatory elements that can be at the root of human hearing and balance disorders.”
The researchers are currently performing experiments on specific lncRNAs to reveal their precise functions within the inner ear sensory epithelium.