In a newly published study led by researchers at Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, a unique sound therapy has shown to reduce symptoms of motion sickness. The technology, which stimulates the inner ear with a specific wavelength of sound, has demonstrated significant effectiveness in alleviating symptoms such as nausea and dizziness, even after a short one-minute exposure.
The study, published in Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine, reveals that sound stimulation at 100 Hz, a frequency found to activate the vestibular system, could provide a simple yet effective treatment for motion sickness. This innovative approach represents a significant advancement in the understanding of how sound can influence the inner ear, particularly in relation to balance and motion sickness.
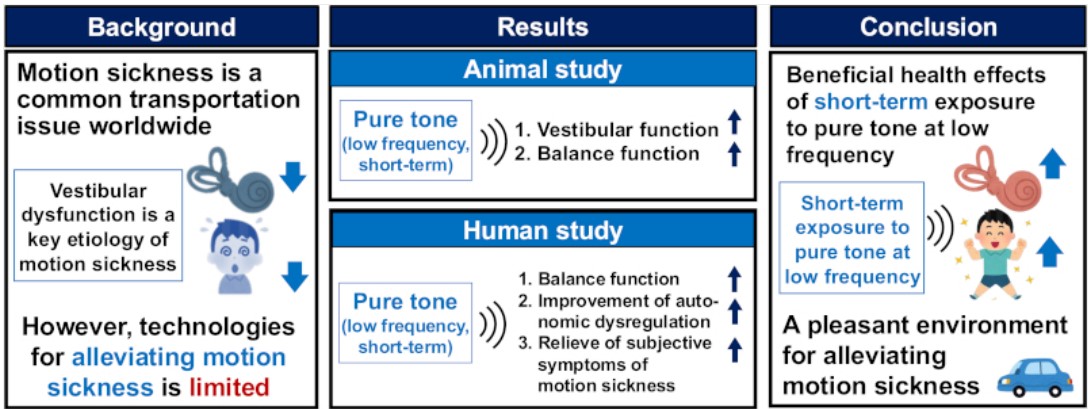
Image credit: Gu, Y. et. al. Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (2025). DOI: 10.1265/ehpm.24-00247
Sound Spice: A Unique Solution for Motion Sickness
The research team, led by Takumi Kagawa and Masashi Kato, explored the potential of a sound stimulation device that exposes individuals to a specific frequency of sound. In their study, participants were exposed to a “unique sound” at 100 Hz, referred to as “sound spice.” The results were promising: within just one minute of exposure to this pure tone, participants reported a reduction in the imbalance and discomfort typically associated with motion sickness during travel.
“Our study demonstrated that short-term stimulation using a unique sound called ‘sound spice’ alleviates symptoms of motion sickness, such as nausea and dizziness. The effective sound level falls within the range of everyday environmental noise exposure, suggesting that the sound technology is both effective and safe.”
–Takumi Kagawa
The breakthrough comes as researchers continue to explore the effects of sound on the vestibular system, which plays a key role in balance. The vestibular organs, including the otolithic organs in the inner ear, help detect linear acceleration and gravity, and their stimulation may hold the key to alleviating symptoms of motion sickness.
Reducing Motion Sickness with Sound Technology
The device works by producing a pure tone at 100 Hz, which activates the vestibular organs in the inner ear, improving balance and alleviating the symptoms of motion sickness. The researchers tested this technology using human participants in various motion sickness scenarios, including being exposed to the movements of a swing, a driving simulator, and an actual vehicle.
In each case, participants who received sound stimulation before being exposed to motion showed improved balance and reduced symptoms of motion sickness. The exposure resulted in lower scores for imbalance and less autonomic dysregulation, as indicated by heart rate variability (HRV) readings. These findings highlight the potential of sound stimulation to alleviate both physical and autonomic symptoms of motion sickness.
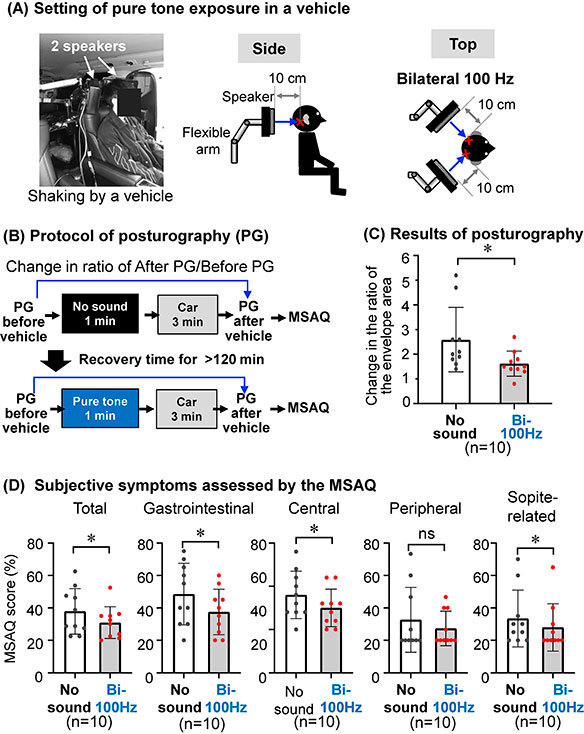
Image credit: Gu, Y. et. al. Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (2025). DOI: 10.1265/ehpm.24-00247
“We found that activation of sympathetic nerves, which are often dysregulated in motion sickness, was objectively improved by the unique sound exposure,” said Masashi Kato, co-author of the study.
The results suggest that this sound-based therapy could become a practical solution for motion sickness in various transportation settings, including air and sea travel. Additionally, the sound exposure technology could be incorporated into existing devices such as hearing aids and other audio devices, potentially offering an accessible and non-invasive treatment option for individuals who frequently experience motion sickness.
Safe, Effective, and Ready for Practical Use
One of the key advantages of this sound therapy is its safety. The sound exposure levels used in the study were well below workplace noise safety standards, and the researchers emphasize that the short duration of the exposure (just one minute) makes it a safe intervention.
“The health risk of short-term exposure to our unique sound is minimal. Given that the stimulus level is well below workplace noise safety standards, this stimulation is expected to be safe when used properly.”
–Takumi Kagawa
As the team continues to refine the technology, the goal is to develop a device that can be used in a variety of transportation environments, such as cars, planes, and trains, to prevent motion sickness and improve comfort during travel. The technology’s application could revolutionize how we address motion sickness, which affects millions of people worldwide.
This research represents just one example of how sound technology can be harnessed for therapeutic purposes. The potential benefits extend beyond motion sickness, as the technology could be adapted to treat other balance disorders, such as those related to Meniere’s disease.
As researchers look ahead, they plan to further develop and test the technology for broader use, aiming to offer a practical solution for alleviating motion sickness in everyday life. In the meantime, the results of this study offer hope for those who struggle with motion sickness, providing a glimpse of a future where sound therapy plays a crucial role in maintaining comfort and balance during travel.
Reference
- Gu, Y. et al, Just 1-min exposure to a pure tone at 100 Hz with daily exposable sound pressure levels may improve motion sickness, Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine (2025). DOI: 10.1265/ehpm.24-00247
Source: Nagoya University, EHPM






