WASHINGTON, D.C. — In recent years, the landscape of hearing aid accessibility in the United States has undergone significant changes. Approximately 38 million American adults report some degree of hearing loss, and an estimated 29 million could benefit from using hearing aids.
Historically, hearing aids in the US have only been accessible through licensed professionals. However, a landmark decision by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in August 2022 allowed the sale of over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids.
The Government Accountability Office (GAO) recently released a study examining how this change has impacted consumer access to hearing loss treatment.
Purpose of the Report
The GAO study was initiated to evaluate consumer access to hearing loss treatment following the FDA’s issuance of the OTC hearing aids Final Rule. The report aimed to describe what OTC hearing aids are, the FDA’s rulemaking process, existing research on the impact of OTC hearing aids, and the oversight provided by FDA and other federal agencies.
Additionally, the report identifies key issues related to the OTC hearing aid market and explores ongoing challenges in accessing hearing loss treatment.
FDA’s Rulemaking Process
The FDA’s Final Rule, effective from October 2022, created a new category for OTC hearing aids, intended for adults with perceived mild-to-moderate hearing loss. This rulemaking process involved collaboration with internal experts and input from external stakeholders, including consumer groups, audiologists, and industry representatives. The goal was to balance safety and effectiveness while addressing an unmet public health need by making hearing aids more accessible and affordable.
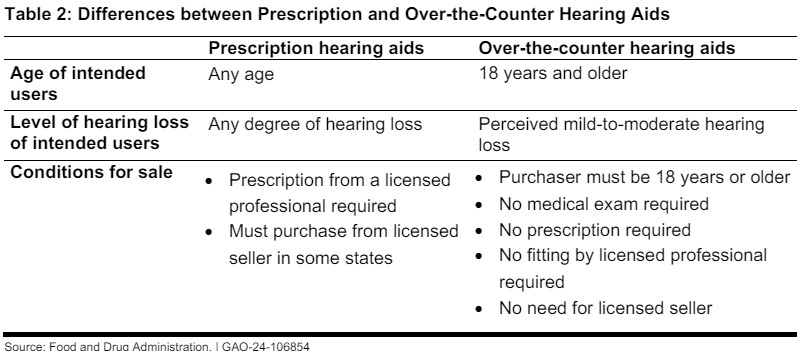
GAO’s Methodology
To conduct this study, GAO reviewed relevant literature, agency documents, and interviewed officials from the FDA and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). The GAO also consulted eight stakeholder groups representing consumers, audiologists, hearing professionals, and the hearing aid industry. These groups were selected based on their engagement with the FDA’s Proposed Rule and their diverse perspectives on hearing health issues.
Key Findings:
Effectiveness and Accessibility
Early research suggests that OTC hearing aids can be as effective as prescription devices, potentially expanding access for those with mild-to-moderate hearing loss. However, the GAO noted that it is still too early to assess the full impact of the Final Rule. FDA officials and several stakeholder groups emphasized the need for more time to gather comprehensive data on the effects of OTC hearing aids on patient access.
Barriers to Access
Despite the promise of increased accessibility, significant barriers remain. Consumer preferences and professional concerns, difficulty in accurately assessing hearing loss, and affordability issues continue to challenge the adoption of OTC hearing aids. For instance, many consumers prefer personalized care from hearing professionals, and some professionals express concerns about the safety and effectiveness of self-fitted devices.

Additionally, the cost of OTC hearing aids, while generally lower than prescription models, can still be prohibitive for some individuals.
FDA and Federal Oversight
The FDA conducts both premarket reviews and post-market surveillance of OTC hearing aids, similar to its oversight of other medical devices. This includes monitoring adverse events and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. The GAO report highlights that, as of early 2024, the FDA had received 12 reports of adverse events related to OTC hearing aids, consistent with expectations based on similar issues with prescription devices. The FTC also plays a role in overseeing advertising practices to prevent misleading claims about OTC hearing aids.
Consumer Education and Market Dynamics
Consumer interest in hearing loss treatment has increased since the introduction of OTC hearing aids. Online searches for hearing aids, particularly those focused on OTC options, have surged.
However, research indicates that many consumers still prefer professional guidance, and some audiologists report an uptick in patients seeking assistance with OTC devices. The GAO report also identifies the importance of clear marketing and return policies to ensure consumers can make informed choices.
Challenges and Future Directions
The GAO report underscores several ongoing challenges in the OTC hearing aids market. Key issues include ensuring accurate marketing, preventing the use of OTC hearing aids by children, and addressing concerns about return policies and device performance. The FDA’s regulations limit the sound output and insertion depth of OTC devices to ensure safety, but some stakeholders believe additional measures, such as gain limits, may be necessary.
Looking ahead, the FDA plans to continue monitoring the OTC hearing aid market and may issue new regulations as technology evolves. The agency is also required to submit a report to Congress by August 2024, analyzing adverse events related to OTC hearing aids, which could influence future regulatory actions.
**Access the full report here.
Source: GAO






