Automobiles are manufactured and driven all over the world. This week at Hearing International we will explore the impact of automobile air bags deployment on hearing. Various types of vehicles are available from the family sedan, station wagon, light pick ups, sport utility vehicles and many other styles. These vehicles may be powered by gas, diesel, natural gas, or a hybrid powered by a combinati0n of electric batteries and gas. Although there are some processes that require a human touch, much of the process in this new century is automated.
Driving these safer vehicles in various parts of the world can be a challenge for both the driver and the vehicle, depending upon the vehicle type, its purpose, traffic, and the type of road that is encountered. The average life expectancy for new vehicles is estimated at 10.8 years as some will go longer, some will crash and others will just wear out our over time.
Cars are lasting longer, becoming more economical and safer for the drivers and their occupants over time, due to better design, building materials, and lots of safety equipment. A review of automobile safety shows one of the worst years in the US for automobile accidents was 1936, when the death rate was almost 3 in every 10,000 people. At that time, auto safety was not considered a priority and safety equipment for vehicles was non existent. Since the 1950s, safety has become a priority in automobile design and the statistics are much better. Although deaths were reduced to some degree in the 1950s and 60s, automobile deaths did not get under 2 in every 10,000 until the 1980s. Since that time the incidence of deaths from automobile accidents, at least in the US, have been reduced to a bit over 1 in every 10,000 people.
While this is an admirable reduction of deaths due to traffic accidents, significant credit has to go to the safety equipment,  automobile design, building materials, seat belts and in particular air bags. These days automobiles are literally crammed with airbags which are deployed as the vehicle hits something from virtually any angle, reducing injury to the occupants. Vehicles in many countries are tested for their road worthiness and to evaluate the danger to the occupants as they are crashed from various angles.
automobile design, building materials, seat belts and in particular air bags. These days automobiles are literally crammed with airbags which are deployed as the vehicle hits something from virtually any angle, reducing injury to the occupants. Vehicles in many countries are tested for their road worthiness and to evaluate the danger to the occupants as they are crashed from various angles.
How do Air Bags Work?
Basically, the air bags work in conjunction with the seat belts to keep the driver from hitting things within the vehicle upon impact.
Although the crash is the primary cause of concern, there is growing interest in the noise levels of these bags when they deploy. What is the mechanism that actuates these bags?
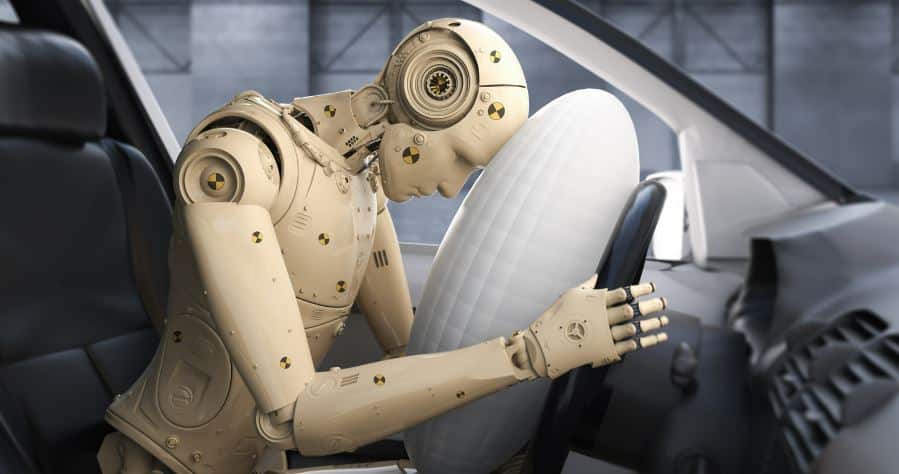
The bags respond to a sensor in the front of the vehicle that when actuated causes the bag to inflate and protects the occupant. Some bags are more sophisticated than others as this technology is constantly updated and modified. The airbag restraint system consists of four major components which work together to slow the passenger’s forward motion as evenly as possible in a fraction of a second.
The parts that make up this restraint system are:
- the airbag
- the air bag cover
- the inflation system
- the sensor
Any defect in these parts could result in an unwarranted injury to the occupant.
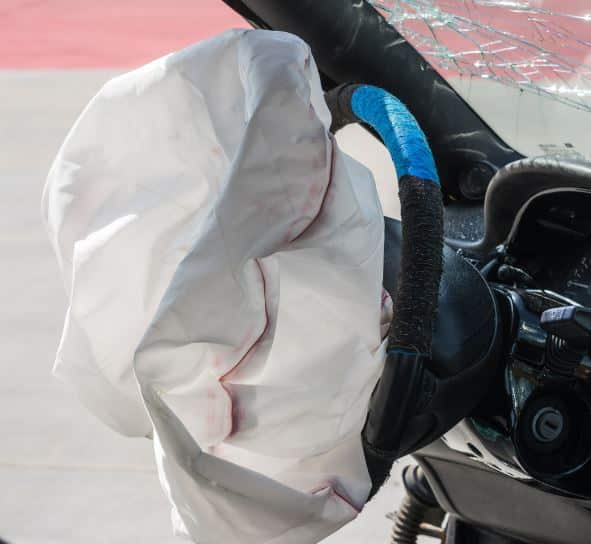 The airbag is made of thin, nylon fabric which is folded into its storage site, located in the steering wheel, dashboard, seat or door. The bag is covered with a dust that consists of cornstarch, chalk, or talcum powder, which provides lubrication during deployment. The bag material is designed to have a degree of porosity. This allows the bag to moderately deflate after inflation, and provide the proper cushioning for the occupant. To protect and hide the air bag system when not in use, a cover over the system is provided. The heart of the airbag system is the inflators. The inflation system design requires the combination of the skills of rocket propellant engineers along with those of auto mechanical engineers.
The airbag is made of thin, nylon fabric which is folded into its storage site, located in the steering wheel, dashboard, seat or door. The bag is covered with a dust that consists of cornstarch, chalk, or talcum powder, which provides lubrication during deployment. The bag material is designed to have a degree of porosity. This allows the bag to moderately deflate after inflation, and provide the proper cushioning for the occupant. To protect and hide the air bag system when not in use, a cover over the system is provided. The heart of the airbag system is the inflators. The inflation system design requires the combination of the skills of rocket propellant engineers along with those of auto mechanical engineers.
These systems have changed substantially over the years, but currently the initiator (sometimes called an igniter or squib) receives an electrical signal from the sensor/electronic module from strategic points on the vehicle, and then it ignites a solid propellant, which burns extremely rapidly to create a large volume of gas to inflate the bag.
Hearing Loss and Tinnitus After Airbag Deployment?
The amount of noise associated with airbag deployment from a car accident varies with the type, size and location of the airbag. Deployment of a driver’s side front airbag will generate mean peak sound pressure levels of approximately 160 dB (decibels). A passenger side front airbag will generate mean peak sound pressure level of 168 dB, while dual airbag deployments create a mean peak sound pressure level of 170 dB.
When you compare these with the level of decibels that can cause hearing loss, the problem becomes evident. Studies have shown that the pain threshold from noise is about 140 dB and that a single exposure to sound pressure of this level can cause permanent, severe hearing loss.
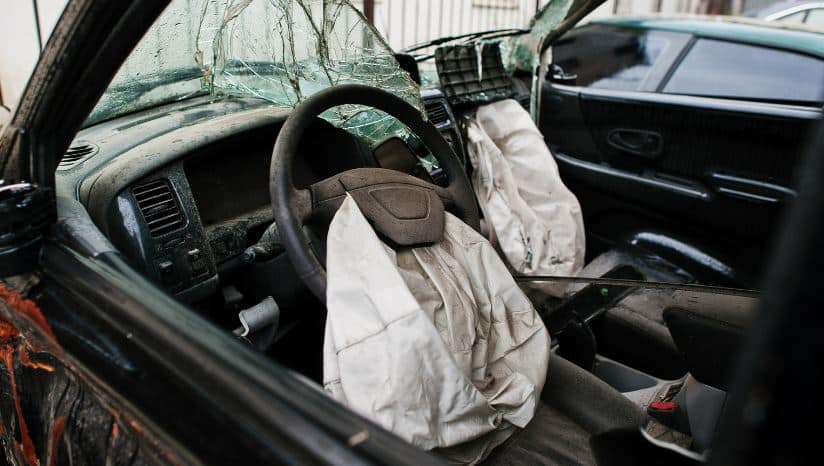

The most recent development of side airbags as optional equipment in some luxury vehicles has only enhanced this problem. The deployment of a side airbag generates a mean peak sound air pressure of 178 dB. That is more than 20% higher than the level necessary to cause permanent severe hearing loss. Add in the fact that the side air bag deploys closer to the ear and the danger becomes escalated.
Ohki, Ishikawa & Tahara (2012) state that the deployment of air bags has been reported to inflict damage on the face, neck, upper chest, and abdomen, for example, eyes, facial nerve, cervical spine, temporomandibular joint, upper airway, lungs, and heart; however, air bag deployment has rarely been reported to cause otologic injuries. Sensorineural hearing loss due to air bag deployment is rare, and there have been only a few reports in the English literature. Audiologists know, however, that 140 dB of intensity is the threshold of pain and these intensities can cause hearing loss under some conditions.
At Hearing International we suspect that a minimal hearing loss from these peak intensities of air bag deployment may be a small price to pay for a life saving device.
About the author

Robert M. Traynor, Ed.D., is a hearing industry consultant, trainer, professor, conference speaker, practice manager and author. He has decades of experience teaching courses and training clinicians within the field of audiology with specific emphasis in hearing and tinnitus rehabilitation. He serves as Adjunct Faculty in Audiology at the University of Florida, University of Northern Colorado, University of Colorado and The University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences.
**this piece has been updated for clarity. It originally published on October 31, 2012







I was in a car accident 1 year ago, and since then I have had many hearing problems including fluid in the ears, ringing, ducks quacking, and hearing loss, My airbags not only deflated but burst and I could not leave the car, so I breathed all the chemicals in. I remember being driven to the emergency room and feeling like I had a river in ears, and could not hear my driver talking to me. Has anyone experienced this?
I had an accident on Saturday which was actually pretty minor (hardly any damage to my vehicle other than airbag deployment and their car’s trunk was a mess – but no apparent physical injuries to anyone), but just today I’ve had ringing start in my ears. It has been 5 days since the accident.
I am researching on subject about The Effect of Automobile Air Bag as you have mentioned in your blog. http://www.cnccenter.com/cnc/fanuc-amplifiers/a06b-61/A06B-6117-H105
Hi i have been involed in a RTA last week, where all the air bag where deployed, since that i have loss the hearing and a constant ringing in my ringht ear.
By the way airbags protect brain from hit i think brain is more important than hearing but airbags and seat belts cant block escape from car.
I was in a terrible accident in 1999. My airbags deployed of course and I have had severe ringing in my right ear since then. The only reason I looked this up this subject now is because the ringing seems to be worse after 14 years. I went to an ENT specialist after the accident. He gave me steroids and a hearing test. The steroids did not help and I had significant hearing loss in my right ear. I also sustained cervical spine injuries. I may have neck pain, constant ringing in my ear and hearing loss but I am still here. If it wasn’t for the seatbelt and airbag I wouldn’t be.
I was in a very minor accident this weekend, but the airbags did deploy. I was driving and my wife was in the passenger seat. Her airbag in our Audi a3 deployed with such force it broke the windshield. Since then I have had a constant ringing in my right ear.