Recent advancements in hearing aid technology have significantly improved communication for individuals with hearing impairments. However, there are situations where additional assistive listening devices (ALDs) become necessary.
ALDs are designed to help individuals with hearing loss in critical listening situations, either as a supplement to or in place of hearing aids. For instance, some users may still struggle with speech comprehension in noisy environments like restaurants, places of worship, or while watching TV. ALDs play a crucial role in addressing these challenges.
One widely used ALD is the caption telephone, along with smartphone applications that offer caption services. Individuals with hearing loss often face challenges using standard telephones, even with hearing aids or cochlear implants, as these devices typically fail to transmit the full frequency range of speech. This limitation poses difficulties for everyone, but it is especially problematic for those with hearing impairments.
Many individuals with untreated hearing loss avoid phone communication or depend on others, leading to isolation and negative health consequences like loneliness and depression.
- Difficulties Using Phone with Hearing Loss
- Captioned Telephone Service (CTS)
- How Phone Captioning Works
- Cost of Caption Phones
- Examples of Caption Phones and Apps
- Captions for Online Platforms
- Smartphone Apps for Captions
- Do I need a Caption Phone?
- Obtaining a Caption Phone – Step by Step Guide
- What to Expect from Captioned Phones
Difficulties Using the Phone with Hearing Loss
 Compared to normal-hearing individuals, those with hearing loss face distinct disadvantages during telephone conversations. The weaker telephone signal, combined with the absence of essential visual cues, hinders effective communication for individuals with hearing loss.
Compared to normal-hearing individuals, those with hearing loss face distinct disadvantages during telephone conversations. The weaker telephone signal, combined with the absence of essential visual cues, hinders effective communication for individuals with hearing loss.
Extensive longitudinal research has indicated that hearing aids may not universally prove effective in facilitating telephone communication for individuals with hearing loss. Surprisingly, this observation seems to be unrelated to the severity of the hearing loss. Although challenges in hearing on the telephone align with the degree of hearing loss, a substantial portion of individuals experiencing mild, moderate, and severe hearing loss report considerable difficulties in telephone communication.
Hearing aids might not effectively assist individuals in communicating over the telephone for various reasons. Presently, slightly over half of consumers express satisfaction with their hearing aids’ performance during phone use. Additionally, consumers report an average benefit of only 55% when using hearing aids for phone conversations.
Although consumer satisfaction correlates with the degree of hearing loss, the benefit appears to be independent of the severity of hearing loss. When surveyed, around 8 out of 10 consumers highly value improvements in the telephone utility of hearing aids.
Moreover, compatibility issues may arise, as some hearing aids may not work seamlessly with all telephones, leading to feedback problems. The presence of telecoils in hearing aids can address such issues; however, not all hearing aids incorporate telecoils, and even when they do, the telecoil may not always be activated, oriented optimally for telephone use, or set to automatic activation. Surprisingly, many consumers may not even be aware of the presence of a telecoil in their hearing aids.
Fortunately, there are means to enhance communication experiences through modern technology. Whether through a cellphone or landline, captioning proves invaluable for improving comprehension during phone conversations and fostering effective communication.
Captioned phones and smartphone apps with captioning features serve as practical solutions to facilitate easier phone communication. Government funding ensures that these phones and apps are accessible either for free or at a substantial discount.

Image credit: CaptionCall
In today’s interconnected world, phones play a crucial role in communication with friends and family. Beyond social connections, phones are indispensable for security and safety, underscoring their essential role in modern life. Thanks to captioned phone calls and/or mobile apps, the days when people with hearing loss were unable to stay connected are a thing of the past.
Captioned Telephone Service
Today, not only hearing people but also individuals with hearing loss can communicate effectively using captioned telephones and cell phone apps. Similar to captioning for movies and TV shows, captioning on a home phone or using smartphone apps provides a real-time transcript of what the person on the other end of the call is saying—allowing for seamless phone calls regardless of hearing ability. Using these products, individuals with hearing loss can remain connected with anyone in the world at any time—safely, quickly, and effectively.
As defined by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC):
“Captioned telephone service allows a person with hearing loss, who can use their own voice and has some residual hearing, to speak directly to the called party. They can then listen, to the extent possible, to the other party while simultaneously reading captions of what the other party is saying.”
Why are caption phones and apps useful?
There are several reasons why captioning phones and apps are useful, including:
- Staying Connected: Captioned phones and apps help individuals with hearing loss avoid social isolation, contributing to improved mental health.
- Occupation: These services support individuals in their professional pursuits, ensuring they can effectively engage in work-related communication.
- Independence: Captioned telephone service promotes independence, allowing users to communicate without relying on others.
- Clearer and Improved Communication: The captions provide a visual aid, facilitating clearer and more effective communication for individuals with hearing loss.
- Safety and Security: Accessible communication tools contribute to the safety and security of individuals, particularly in emergency situations.
How Phone Captioning Works
Individuals with hearing loss can easily access captioned telephone services without the need for a special number or new phone line. Whether using a landline or a dedicated app, the captioned phone automatically connects to a Captioned Telephone Service (CTS) when a call is initiated. As the recipient answers, the caller hears their response just like in a traditional telephone call, with audio customization available to match the consumer’s hearing loss profile.
Simultaneously, the CTS employs advanced voice recognition technology and trained communications assistants to transcribe spoken words into captions, which appear almost instantly on the phone display. This dual functionality allows individuals with hearing loss to both hear and read the conversation during a telephone call. The text size is adjustable, catering to the needs of the elderly, who may experience both visual and auditory impairments as they age.
Modern captioned telephones utilize internet protocol captioned telephone service (IPCTS) to transmit captions via the internet. This improves communication speed compared to earlier devices that required multiple phone lines or a second phone number. Users can retain their existing phone numbers, providing a lifeline for emergency calls and maintaining connections with family and friends. Captioning security is ensured through an encrypted transcription process regulated by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC).
Cost of Caption Phones
The service is cost-free for individuals with hearing loss, thanks to a program funded and administered by the FCC. Operating like a regular phone, ADA guidelines for hearing loss enable free captioning services, often with the phone itself provided at no cost or a discount for landline connections. The FCC’s Telecommunications Relay Service (TRS) Fund reimburses companies offering relay services and landline phones, as regulated by the FCC’s Telephone Relay Services.
To access these complimentary services, individuals generally need to register, confirming their hearing loss that requires captioned telephone assistance. Federal regulations prevent the use of captioned telephone services by individuals without a hearing loss necessitating the service.
It’s important to note that this service differs from the IP (Internet Protocol) Relay Service, which allows a similar service via a smartphone or other device. Smartphone costs are separate from the captioning service.

Examples and Types of Captioned Phones and Apps
Various phone companies offer captioned phones and apps designed for smartphones and tablets, catering to individuals with hearing loss. Some noteworthy options include:

Hamilton CapTel 2400i
1. Hamilton CapTel
- User-friendly captioned telephone with a button-activated caption display.
- Models suitable for those with low vision.
- Excellent for users without internet access, utilizing a standard telephone line.
- Large display with easy-to-read font, hearing aid compatible, and adjustable font sizes.
2. Hamilton CapTel 2400i
- Internet connection option, Bluetooth capabilities, speakerphone, touchscreen, and volume adjustment.
- Popular caption phone with a large touchscreen display.
- Adjustable volume settings (up to 40 dB), caller ID, and an answering machine.
- Internet-dependent, requiring a stable phone line and high-speed internet.
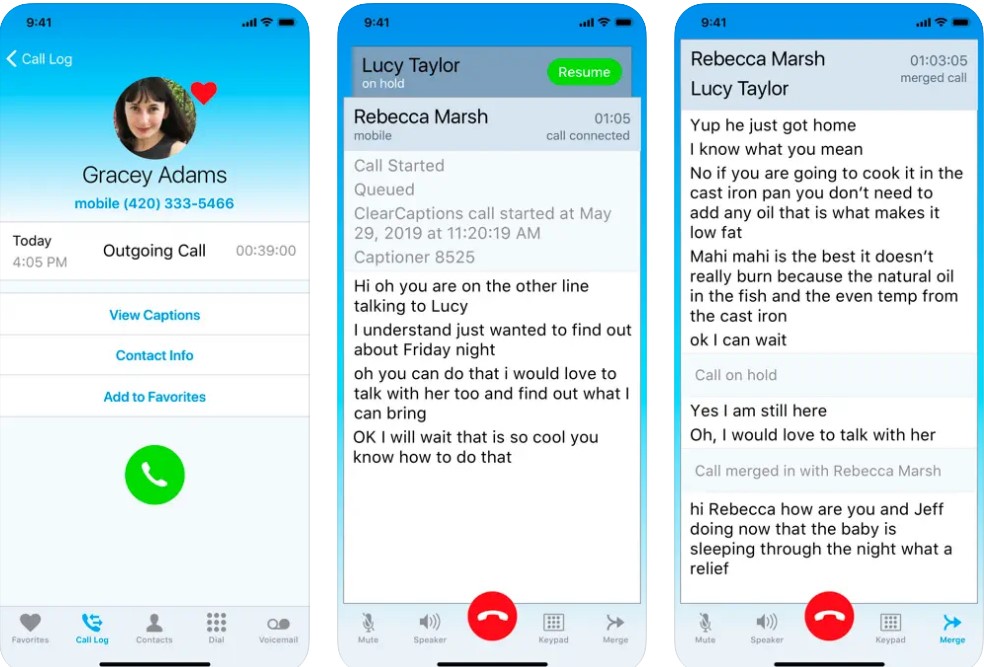
3. ClearCaptions
- Features an amplified home phone with near real-time captions on an 8-inch color touchscreen.
- ClearCaptions Mobile app offers call captioning and a personalized ClearCaptions Number.
4. CaptionCall
- Sleek design, state-of-the-art captioning, and telecoil loop connection for hearing aid users.
- Allows saving conversations and previous volume settings for efficiency.
- CaptionCall Mobile (formerly called Olelo) is their mobile app.

Captioning Options for Online Platforms
Online platforms are widely used today, especially in the workplace, and can run off a tablet or smartphone for increased accessibility. They also have captioning features that allow for ease of communication and understanding while communicating on these platforms.
Furthermore, the user has access to video call, which can provide visual cues that can assist with speech understanding. The use of these platforms are free and require a stable internet connection for best results.
- Microsoft Teams:
- Microsoft Teams offers built-in live captioning during meetings and calls.
- To enable captions:
- During a meeting, click on the ellipsis (three dots) in the meeting controls.
- Select “Turn on live captions.”
- Captions will start appearing on the screen.
- Google Hangouts:
- Google Hangouts does not have built-in live captioning.
- Users may consider third-party applications or services that provide real-time transcription for Google Hangouts meetings.
- Skype:
- Skype provides live captioning for both video and voice calls.
- To enable captions:
- During a call, click on the “+” more options menu.
- Select “Turn subtitles on.”
- Captions will be displayed on the screen
Similar options are available on Zoom as well, thanks to significant levels of advocacy during the pandemic, and further details can be accessed here.
These platforms strive to enhance accessibility by incorporating live captioning features, making virtual communication more inclusive for individuals with hearing loss.
Smartphone Apps for Captions
Smartphone applications have become essential tools for individuals with hearing loss, especially in situations like a global pandemic that limits face-to-face interactions. Here are some caption apps available for both iOS and Android devices:
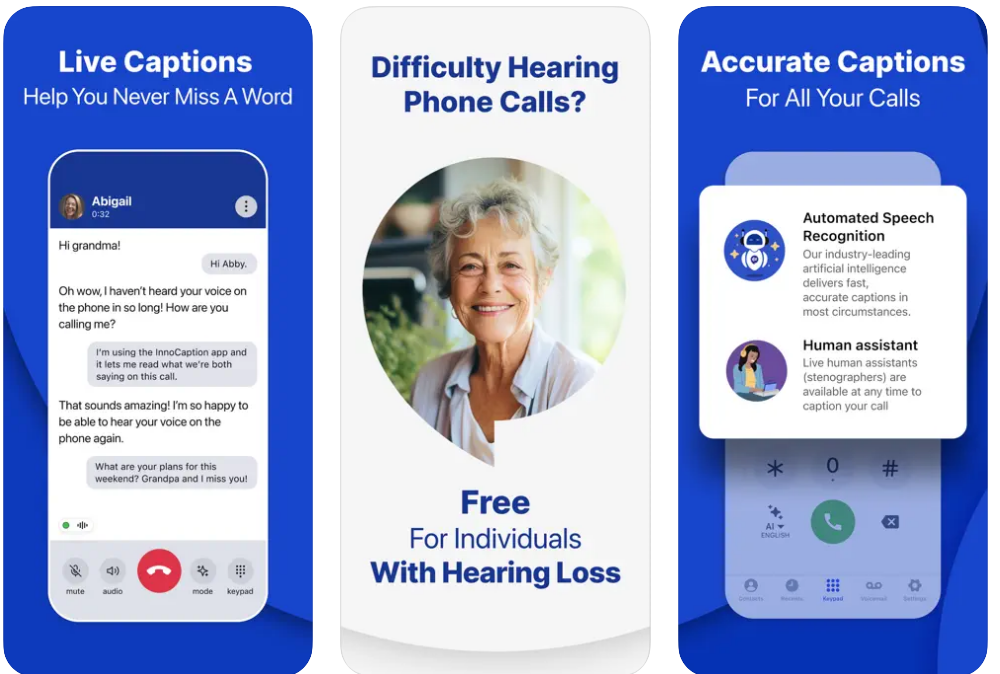
- InnoCaption
- Android & iOS
- Free captioning service funded by the FCC.
- Real-time captioning on mobile devices.
- Developed with live stenographers for fast, easy, and accurate captioning.
- Users need to register and self-certify hearing loss.
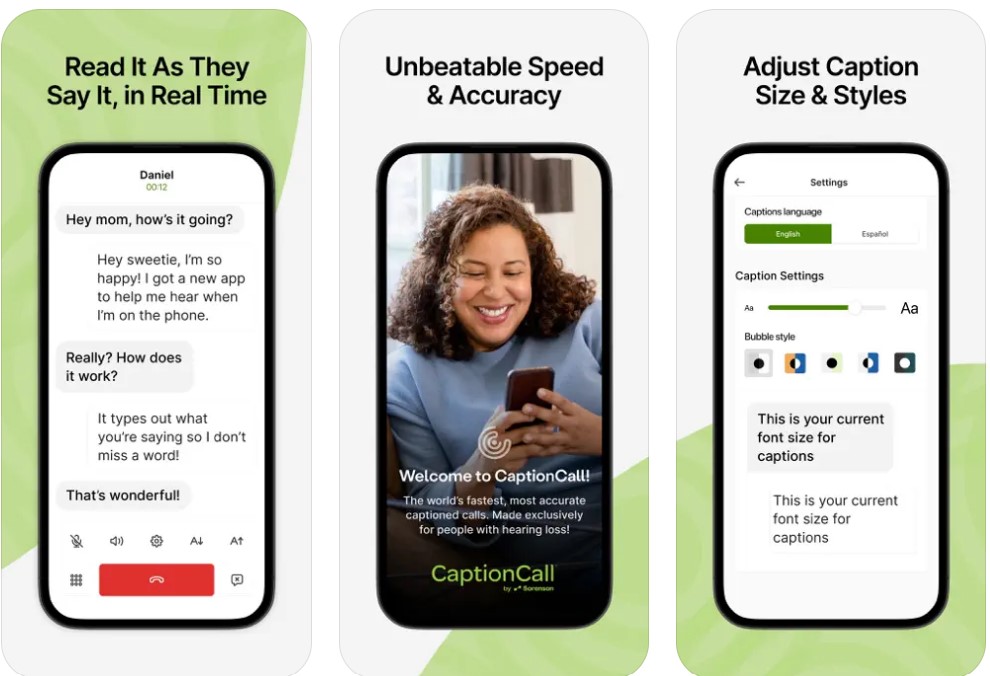
- Ava
- Android & iOS
- 5 hours free per month, payment plans available.
- Transforms a smartphone’s microphone into a captioning service.
- Requires a good Wi-Fi connection and works with Bluetooth devices.
- Allows sharing QR codes for multi-user conversations.
- Offers a text-to-speech feature and saves conversations for later review.
- CaptionMate
- Android & iOS
- Instant transcription of phone calls on various devices.
- Real-time captioning service, free for those with hearing loss.
- Captions over 100 languages and saves conversations for later.
- Rogervoice
- Android & iOS
- Live subtitles calls in over 80 languages.
- Displays speech as text instantly.
- Allows speech or text replies and captions incoming calls.
- Pricing plans start at $5.99.
- CaptionCall Mobile
- Android & iOS
- Live captions of conversations and voicemail.
- Uses automatic speech recognition technology.
- Saves conversations in transcript form.
- Available in English or Spanish and funded by the FCC.
Caption Apps for Apple iOS Only:
- Hearing Helper – Live Captions
- iOS only
- Utilizes Apple’s Siri technology for speech-to-text translation.
- Ideal for communicating with HOH, Deaf, or ESL individuals.
- Allows recording, editing, and text enlargement.
- Hamilton CapTel
- iOS only
- Free mobile application for those with trouble hearing on the telephone.
- Provides word-for-word captions of phone conversations.
- ClearCaptions Mobile
- iOS only
- Offers real-time captioning on mobile phones.
- FCC-certified service for qualified individuals with hearing loss.
- Provides a free account with a personal ClearCaptions voice phone number.
Apps for Android Only:
- Live Transcribe & Sound Notification
- Android only
- Developed by Google in partnership with hearing loss experts.
- Provides free, real-time transcriptions and sound notifications.
- Available in 80 languages with additional features.

These caption apps cater to diverse needs, fostering inclusivity in health-related engagements and everyday communication.
Do I need a Caption Phone?
If you find yourself grappling with any of the following challenges, it might be time to consider a caption phone and take a hearing test to address your unique hearing needs:
- Difficulty Hearing Over the Telephone: Struggling to hear clearly during phone conversations.
- Challenges in Group Conversations: Finding it hard to follow discussions when multiple people are talking simultaneously.
- Frequent Requests for Repetition: Often asking others to repeat what they’ve said.
- High TV Volume Complaints: Increasing the TV volume to levels that bother others.
- Hearing Issues in Background Noise: Experiencing difficulty hearing due to surrounding noise.
- Perception of Mumbled Speech: Feeling that others speak unclearly or mumble.
By recognizing these symptoms, it’s crucial to consult with a hearing care professional. They can conduct a comprehensive hearing test, identify your specific hearing challenges, and provide guidance on potential solutions. Additionally, they can recommend suitable caption services tailored to your individual communication needs, ensuring an optimal hearing experience.
Obtaining a Caption Phone: A Step-by-Step Guide
If you’re considering a caption phone, the process is straightforward, ensuring you can enhance your communication experience effectively.
- Seek Assistance:
- Connect with your hearing care provider for guidance or directly approach a captioned telephone retailer.
- Choose a Provider:
- Opt for a company offering caption phones. Some providers offer complimentary delivery, installation, setup, and user training.
- Verify Eligibility:
- To qualify for the free option, ensure you meet eligibility criteria and provide a certified form signed by a hearing care practitioner.
Steps to Obtain a Free Caption Phone:
- Select a reputable caption phone company.
- Certify your hearing loss necessitates captioned telephone service.
- Follow the guidance of the chosen company in the qualification process.
- Complete a form, signed by a medical professional or audiologist.
Preparation Checklist:
- Medically recognized hearing loss.
- High-speed internet connection (if applicable).
- Standard home phone and electrical outlet.
Installation Process:
- No additional charges for delivery and installation.
- A local trainer will install and ensure the phone functions, providing user training.
- The trainer completes necessary paperwork for FCC compliance.
Considerations When Choosing Caption Phone:
- Ease of Use:
- Evaluate user experience, visibility, screen brightness, and menu accessibility.
- Features:
- Check for adjustable volume controls, speakerphone, and noise reduction features.
- Service and Support:
- Confirm available support resources like chat, phone, or email.
- Cost:
- Explore cost-effective options, including free or low-cost choices.
Drawbacks of Caption Telephones/Services:
- Speed: Captioning services may have processing delays.
- Accuracy: Occasional inaccuracies in captioning, but overall, it remains a valuable tool for staying engaged in conversations.
What to Expect from Captioned Phones
Captioned telephones offer a range of benefits, making them accessible, affordable, and user-friendly, whether used with or without hearing aids. While these assistive devices aren’t flawless, providing captions with a slight lag and occasional minor inaccuracies, users often find significant improvements in their communication experience.
Key Features:
- Availability: Easily accessible and readily available.
- Affordability: Relatively inexpensive, making them a cost-effective solution.
- User-Friendly: Simple to use, catering to both hearing aid users and those without.
- Potential Lag: Users may experience a slight delay in captions.
- Occasional Inaccuracies: Captioning might occasionally have minor errors.
Transformation in Communication:
- Restored Confidence: Many users regain confidence in phone conversations, overcoming years of avoiding calls or pretending to understand.
- Reconnection: Users feel reconnected with distant relatives and friends.
- Workplace Support: Offices often provide captioned phones for deaf or hard-of-hearing employees.
Variety of Models and Features:
- Answering Machine/Voicemail: Depending on the model, many captioned phones offer an integrated answering machine or voicemail service for saving and reviewing messages.
- Custom Phone Book: Users can create a personalized phone book to store favorite contacts.
- Visual Alerts: Features like a bright flashing light signal incoming calls visually.
- Font Customization: Adjustable font sizes to cater to individual preferences.
- Background Options: Capability to choose between bright or dark background settings.
Transitioning to a captioned telephone not only enhances communication but also provides practical features for personalized and convenient use.
When addressing your hearing needs, opting for a reliable and high-quality caption phone is crucial. With the continuous advancements in technology, exploring caption apps on your mobile phone can also deliver similar benefits. It’s essential to recognize that communication should never be hindered, and the availability of caption-enabled phones serves as a valuable bridge to overcome any gaps.

Key Considerations when Choosing Caption Phone:
- Personalized Solutions: Captioned phones, tailored to individual hearing requirements, offer a customizable speech signal translated swiftly into text format.
- Functional Accessibility: These phones provide a viable and functional solution for individuals experiencing hearing loss.
By making informed choices aligned with your specific needs, you empower yourself to navigate the world of communication seamlessly. Whether through dedicated caption phones or innovative caption apps, the goal remains the same: ensuring that communication remains inclusive and barrier-free for everyone
Resources:
References:
- Hearing Loss Association of America. (n.d.). Phones & Mobile Devices. Retrieved from https://www.hearingloss.org/hearing-help/technology/phones-mobile-devices/
- Healthy Hearing. (n.d.). The Best Phone Captioning Apps for the Hearing Impaired. Retrieved from https://www.healthyhearing.com/report/47850-The-best-phone-captioning-apps-for-the-hearing-impaired
- CapTel. (2019, April). Types of Hearing Impaired & Hearing Loss Telephones. Retrieved from https://www.captel.com/2019/04/types-of-hearing-impaired-hearing-loss-telephones/
- The Hearing Review. (n.d.). The Importance of Captioned Telephone Service in Meeting the Communication Needs of People with Hearing Loss. Retrieved from https://hearingreview.com/hearing-products/the-importance-of-captioned-telephone-service-in-meeting-the-communication-needs-of-people-with-hearing-loss
- Kochkin, S. (2013). The importance of captioned telephone service in meeting the communication needs of people with hearing loss. Hearing Review, 20(3), 28-35.
- National Association of the Deaf. (n.d.). Captioned Telephone Service (CTS). Retrieved from https://www.nad.org/resources/technology/telephone-and-relay-services/captioned-telephone-service-cts/
- Association of Late-Deafened Adults. (n.d.). Caption Telephones and Cell/Mobile Apps. Retrieved from https://alda.org/caption-telephones-and-cell-mobile-apps/
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2020). The Impact of Captioned Telephones on Social Participation and Well-being in Older Adults with Hearing Loss. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7744170/
- The Hearing Journal. (2023, April). Telephones Are Not Just for Texting. Retrieved from https://journals.lww.com/thehearingjournal/Fulltext/2023/04000/Telephones_Are_Not_Just_for_Texting.7.aspx
- AudiologyOnline. (n.d.). The Importance of Television Closed Captioning and Telephone Captioning for People with Hearing Loss. Retrieved from https://www.audiologyonline.com/articles/importance-television-closed-captioning-and-22082
About the Author
 Nausheen Dawood is an experienced Audiologist and Project Manager with a professional background including primary health care, corporate social investment, and business development. Proficient in the development of academic courses, training, and lecturing, with a focus on clinical student training and supervision. Adept in freelance copywriting, particularly in audiology and health-related topics. Holds a Masters degree in Audiology (Cum Laude), with a strong foundation in clinical research, project development, and strategic planning, complemented by technical training. Specializes in content development and training tailored to diverse audiences. Demonstrates a long-term commitment to research and development, including the implementation of randomized controlled trials, projects, and clinical examinations. Known for establishing robust networks and cultivating valuable stakeholder relationships.
Nausheen Dawood is an experienced Audiologist and Project Manager with a professional background including primary health care, corporate social investment, and business development. Proficient in the development of academic courses, training, and lecturing, with a focus on clinical student training and supervision. Adept in freelance copywriting, particularly in audiology and health-related topics. Holds a Masters degree in Audiology (Cum Laude), with a strong foundation in clinical research, project development, and strategic planning, complemented by technical training. Specializes in content development and training tailored to diverse audiences. Demonstrates a long-term commitment to research and development, including the implementation of randomized controlled trials, projects, and clinical examinations. Known for establishing robust networks and cultivating valuable stakeholder relationships.






